Almost all electronic financial markets trade based on an auction market. Understanding how financial auction markets operate is paramount for anyone interested in becoming a successful trader. In traditional auctions an auctioneer conducts the auction process. Typically the auctioneer will start the auction process at an open price. If the open price is perceived as reasonable value, auction participants respond by accepting it. The buyers acceptance of the price will prompt the auctioneer to raise the offered price. The auctioneer will continue to move the price higher until there are no more buyers willing to buy at that high price level. At that point the auctioneer will quickly pronounce the item sold to the highest bidder.
If there are no buyers interested at the auction open price, auctioneer will bring the price down until one of the auction participant shows interest. The dynamics of the auction market may quickly change based on what is perceived as value. Consider the following property foreclosure auction. Initial open price for a million dollar home started at $650K. No one was interested in the property at that price. The auctioneer dropped the opening bid to $600K. There was still no interest in the property. He continued to drop the bid lower to $550K, then to $500K and so on until a buyer finally stepped forward at $300K. At this point other bidders start to participate in the auction and the price began to go up. It moved from $300K all the way up-to $600K . This example shows how quickly things can change in any auction and how prices will adjust to supply and demand.
Financial markets use the same auction theory and principles as traditional auctions even thou the mechanics of the auction are quite different. Financial auction market is continuously responding to the available orders in the market. Once the market opens for an instrument like stock, there are usually large number of orders already placed in the Order Book. The price will move up and down in a price ladder to facilitate trade and fill as many orders as possible. The response of the market participants determine the direction and pace of auction activities.
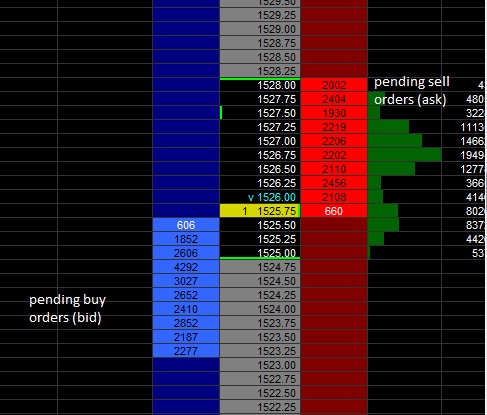
The Order Book is an important element of the financial auction market. There are 3 levels of access to the actual Order Book for any instrument. Level I provides number of bid and ask orders at the current price. Level II offers a larger but still limited view of the bid – ask spread. Level III offers an open view of the entire Order Book. Level III access is only available to market makers and dealers.
The Order Book is the roadmap for the financial auction process. The number and size of the orders in the book determines the direction and speed of the auction process. Market participants that are interested in buying place their orders on the bid side of the book and sellers will place their orders on the ask side. Sellers will offer to sell to the market at the ask. The ask is the price seller is demanding from the buyer to make the sale. Sometimes the ask is also referred to as the offer. On the opposite side buyers present a bid price to sellers. Bid price is the amount buyer is willing to pay to the seller to make a deal. If the bid and ask prices are not equal, no transactions will take place. The difference in price between the bid and ask price is known as the spread.
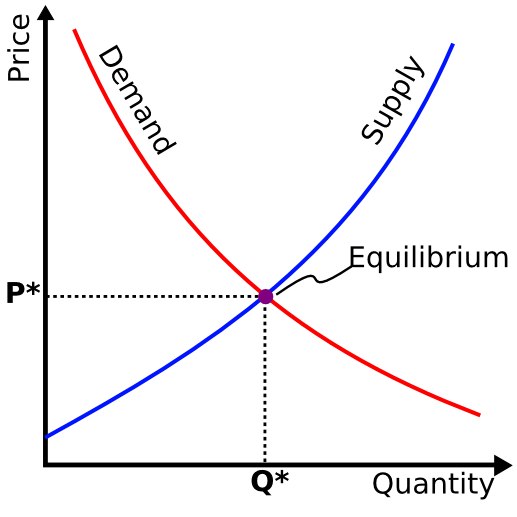
Supply and demand is perhaps one of the most fundamental concepts of economics and it is the backbone of a market economy. Demand refers to how much quantity buyers are willing to buy at a certain price. The relationship between price and quantity demanded is known as the demand price relationship. Supply represents the quantity sellers are willing to sell at a particular price. The correlation between price and quantity offered to sell is known as the supply price relationship. Price is a reflection of supply and demand.